Climate and Geography
Senegalese climate
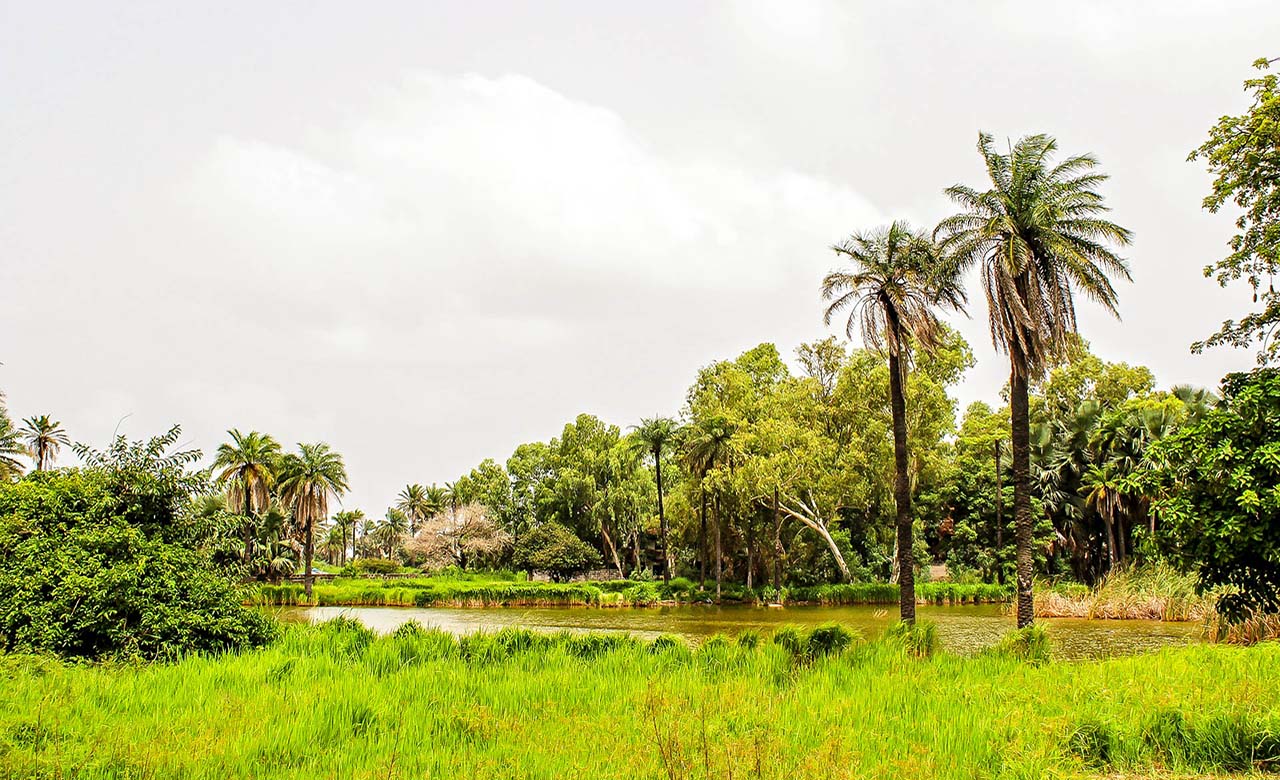


Senegal is located in the intertropical zone with two major climatic domains. We distinguished between the desert climate in the north and the tropical climate in the south.
The Desert climate in the north
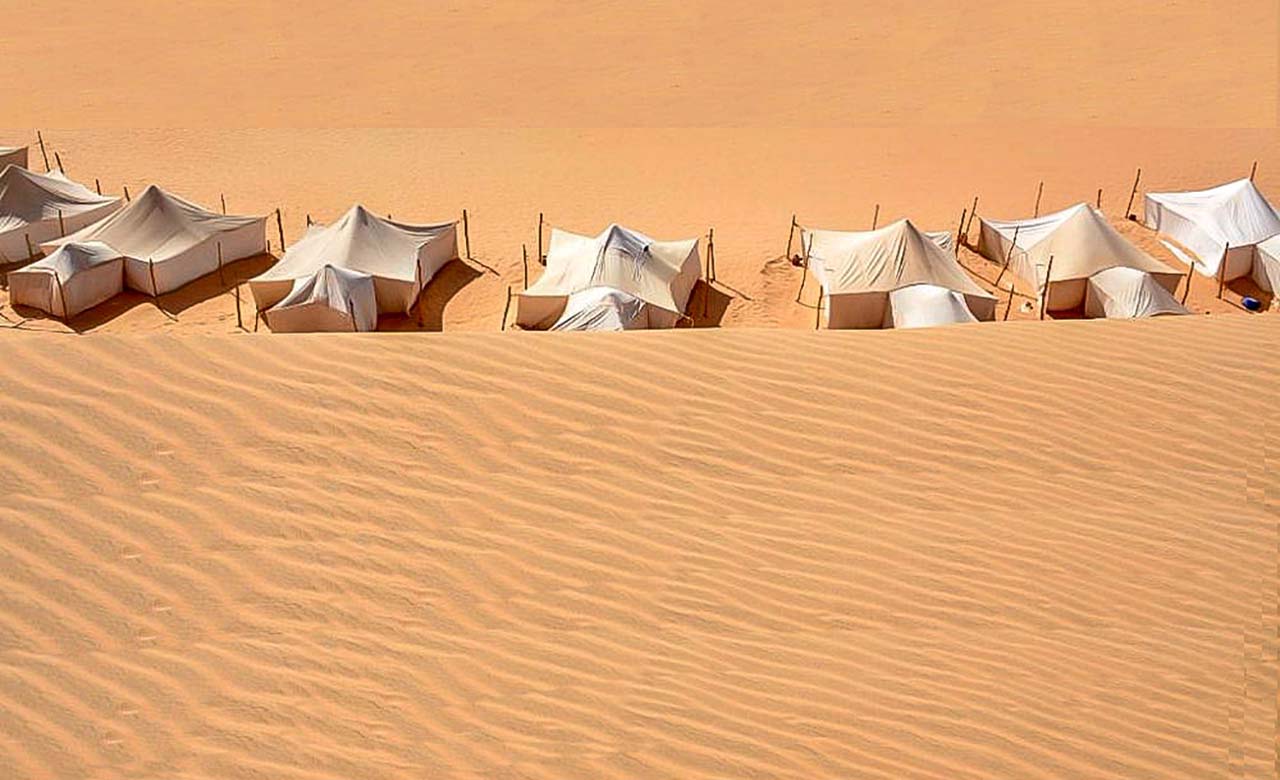

The desert climate is characterized by drought all year round. Temperatures are different in cold deserts and hot deserts. Low rainfall affects vegetation: vegetation is rare and if present is adapted to permanent drought. There are often temporary pasturelands in which the nomads practice their route transhumance with their flocks. Oases are water points that permit mankind to settle down. The oases permit date palms to grow. The date palms produce dates and provide shade for crops. Animal life is not absent in the deserts: in effect, we find mammals (jackal, fennec, etc.), insects, reptiles (snakes) and birds in the deserts.
The Tropical climate in the south

The tropical climate is characterized by the existence of two seasons, the wet season and the dry season, which share the year in an unequal manner depending on the region. A long dry season that runs from November to June and a wet season that goes from July to October, which is even longer in Casamance. However, from the coast of Saint-Louis through the Cape Verde peninsula is subjected to the trade winds during the dry season. The mean temperature is 23 ° C in January and 28 ° in July. Annual precipitation is higher in the south with an average of 1400 mm.
The vegetation
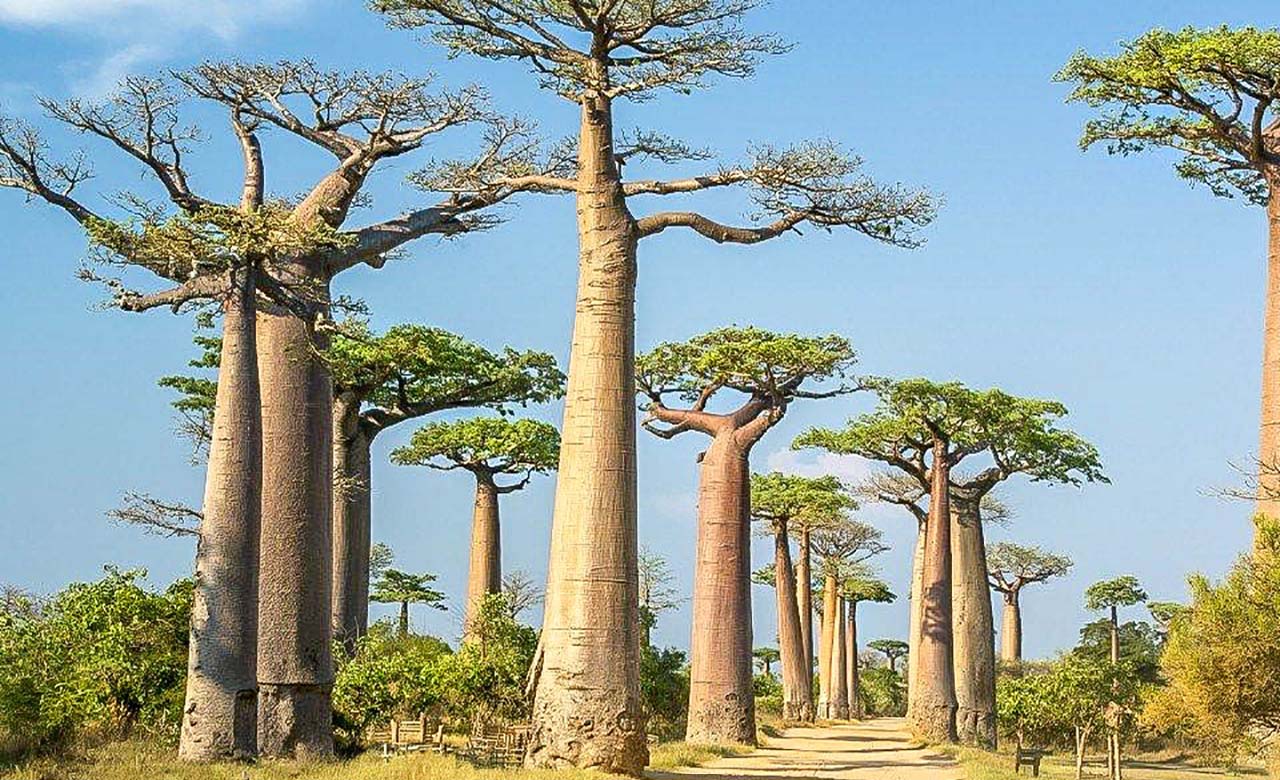

Due to the many climatic zones, Senegal is divided into several vegetation zones. Senegal offers a mosaic of ecosystems including steppes, savannahs, forests and mangroves.
The steppes: It covers nearly one-third of the northern part of the country. It is spread over the sandy soils. They are made up of a more or less continuous grassy carpet, which is dominated by plant species such as Acacias, various varieties of Cenchrus and several other animal species
The savannahs: They cover one third of the national territory, and are made up of the arboreal and arbustives savannahs. They are characterized by woody species such as Cordyla pinnata, Ficus sycomorus, Diospyros piliformis and many other plant species.
The Forests: They are generally found in the south of the country with clear/open forests, dense dry forests and dense gallery forests. The open forests are located in Upper and Middle Casamance while the dense dry forests are mainly located in low Casamance.
Mangroves: These are true marshy/swampy ecosystems. They are impenetrable forests as a result of the mangroves occupying the downstream parts of estuaries, deltas and the main mouths of rivers. They develop in the areas where there are tidal fluctuations and consist of several species.
Geography of Senegal